The PharmacoMicrobiomics web portal is a part of an initiative to explore the interactions between human-associated microbes (human microbiome) and drugs by building a knowledgebase that allows interested students and investigators "to predict the behavior of untested members of drug classes or unstudied microbial species, and to design laboratory experiments for testing these predictions. (More in BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12(Suppl 7):A10)
What to Find Here?
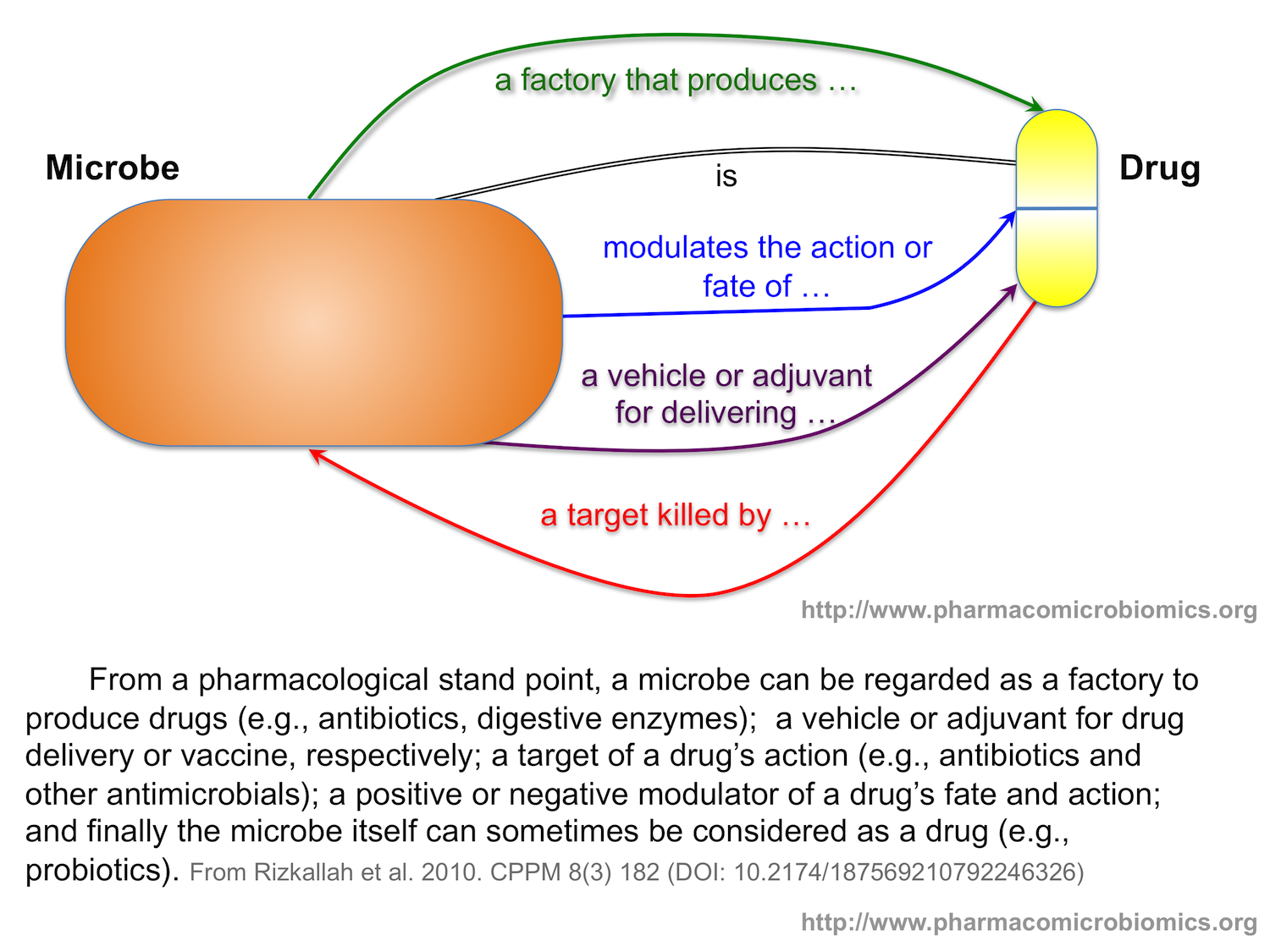
You will be able to find different types of information mostly related to the effect of microbes on drugs (more specifically on the effect of human microbiota on drug disposition or pharmacokinetics). In the future, there may be more information about more complex drug-microbe interactions, and about microbes as drugs, drug factories, or drug-delivery vehicles.
You now can find several entries in the database, including:
- a list of drugs with entries in the database
- the actual list of all body site-drug-microbe interactions
- a list of references to publications describing body site-drug-microbe interactions. Many of those publications have been already curated in the "relations" table, but some of them are not.
You can also find more entries still in "draft" format (mostly Google Docs) that describe a long reading/task list for our current or future curators, and also for those community volunteers who are willing to join our efforts.
Random Interaction
| Urogenital tract | |
| tenofovir (464205) | |
| Gardnerella vaginalis (2702) | |
| 28572388 (Year: 2017) |
|
| increase metabolic processing | |
| The vaginal microbiota significantly modulated the microbicide efficacy of tenofovir gel. Specifically, in women with a Lactobacillus-dominated vaginal microbiota, tenofovir effectively reduced HIV incidence by 61%. However, in women whose vaginal microbiota was dominated by Gardenerella vaginalis and other anaerobes, the drug was more or less ineffective (a non-significant incidence reduction of 18%, with p-value = 0.644). In the latter group (non-Lactobacillus group), detectible mucosal tenofovir levels were lower. Thus, Gardnerella vaginalis and other anaerobes are believed to have depleted tenofovir by metabolism. (See record) |
Credits
This drug-microbiome database was designed and built as the graduation project of the Open Source Technologies track at the Information Technology Institute (ITI) in June, 2011.
Django, the Python-based framework, was used to build the web portal, and JQuery libraries. JLinkPreview plugin is provided by Sarpdoruk Tahmaz. This template is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License by Arcsin Web Templates. The project was hosted by WebFaction (2011-2021). It is currently hosted by Digital Ocean.